Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) of the brain is one of the most advanced diagnostic tools in modern medicine. Using a powerful magnetic field and radio waves without any radiation exposure, it produces highly detailed images of the brain and surrounding structures. Neurologists rely on the brain MRI procedure to detect, monitor, and treat a wide range of neurological conditions, including stroke, tumours, and multiple sclerosis.
At Venkateshwar Hospital, the brain MRI procedure is performed with advanced imaging technology and specialist expertise to ensure both accuracy and patient comfort. This guide explains what the procedure involves step by step and why neurologists often prescribe it.
What is a Brain MRI?
The brain MRI procedure uses powerful magnets, radio waves, and computer technology to create precise, high-resolution images of the brain. Unlike X-rays or CT scans, an MRI does not use ionising radiation, making it a safer option for detailed imaging. Doctors recommend it when they need to identify tumours, infections, bleeding, or neurological disorders with great clarity.
At Venkateshwar Hospital, patients benefit from a wide range of MRI specialisations, such as:
- Neuro Imaging – for detecting stroke, brain tumours, infection, parasites, underlying cause of is seizure disorder and nerve-related conditions.
- Musculoskeletal Imaging (MSK) – for injuries or disorders of bones, joints, and soft tissues, tumours, deformity, syndrome, spectrum of seronegative arthropathy.
- Body Imaging – for abdominal and pelvic organs, including all spectrum.
- Breast Imaging – for early detection of breast cancer and other conditions.
- Foetal MRI – for detailed imaging of unborn babies when required.
- MR Angiography & Venography – for visualising blood vessels and blood flow, and for identifying thrombi and vascular anomalies.
- MR Perfusion Study – for assessing blood flow to tissues and detecting strokes, ischemia, tumours, or other perfusion abnormalities.
These advanced imaging techniques ensure that every patient undergoing a brain MRI procedure receives accurate and detailed results for better treatment planning.
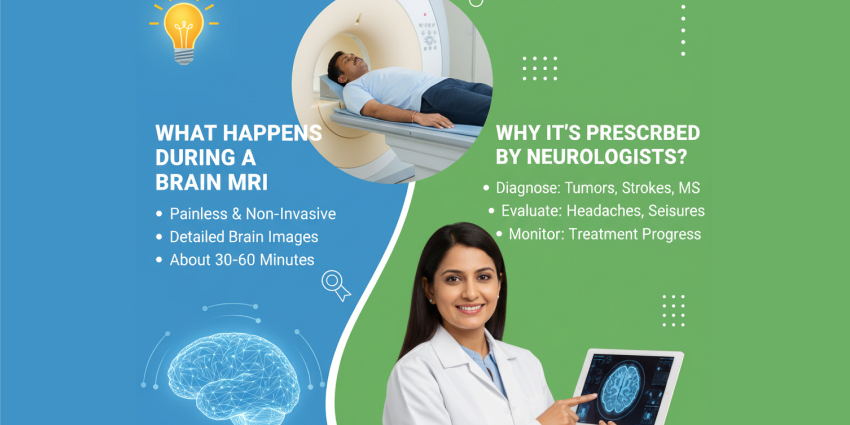
What Happens During a Brain MRI Procedure?
The brain MRI procedure is performed in several key steps to ensure safe and accurate results.
1. Preparation
- If you have a pacemaker, cochlear implant, metallic implants, or any implanted medical device, consult your doctor before undergoing an MRI scan.
- You will lie on a motorised table that slides into the MRI scanner.
- All metallic objects, such as jewellery, watches, or hairpins, must be removed.
- A head coil is placed around the head to capture detailed images.
- Earplugs or headphones are provided to minimise noise discomfort.
- In some cases, a contrast dye may be injected into a vein to highlight specific tissues or blood vessels.
2. Scanning
- The MRI machine’s magnetic field aligns hydrogen atoms in the brain.
- Radio waves briefly disrupt this alignment, and as the atoms return to normal, signals are produced.
- These signals are converted into detailed images by the computer system.
3. Image Acquisition
- A radiographer operates the scanner from a separate room.
- Communication is maintained through an intercom, and patients are given a call button for safety.
- Remaining still is essential to avoid blurry images.
4. Duration
- A typical brain MRI procedure takes 20 to 60 minutes.
- Time may vary depending on scan complexity, use of contrast, and patient movement.
Why Do Neurologists Prescribe Brain MRIs?
Neurologists recommend the brain MRI procedure for multiple reasons, including diagnosis, monitoring, and treatment planning.
- Diagnosing Neurological Conditions
Helps identify tumours, multiple sclerosis, stroke, infections, and vascular abnormalities. - Evaluating Brain Injuries
Reveals damage caused by trauma, haemorrhage, or reduced blood supply. - Monitoring Disease Progression
Tracks conditions like multiple sclerosis over time. - Guiding Treatment Plans
Used for pre-surgical mapping, radiation therapy planning, and personalised treatment strategies. - Differentiating Brain Tissues
Distinguishes between white matter, grey matter, cerebrospinal fluid, and blood vessels. - MR Perfusion Imaging – for assessing blood flow to tissues and detecting strokes, ischemia, tumours, and perfusion abnormalities.
- MR Spectroscopy – for evaluating the chemical composition of tissues, helping in the diagnosis of brain tumours, metabolic disorders, and other neurological conditions.
What to Expect After the MRI?
- Most patients can resume normal activities immediately.
- If contrast dye is used, mild effects such as a metallic taste or slight bruising at the injection site may occur.
- A radiologist reviews the images and shares the report with your neurologist within one to two days.
Risks and Limitations of Brain MRI
While the brain MRI procedure is generally safe, there are some considerations:
- Claustrophobia in the enclosed scanner may cause anxiety.
- Loud machine noises can be uncomfortable, though ear protection is provided.
- Rare allergic reactions to contrast agents may occur.
- Very tiny abnormalities or certain conditions may not always be detected.
Benefits of the Brain MRI Procedure
The brain MRI procedure offers several advantages:
- Non-invasive and painless.
- Produces highly detailed brain images.
- No exposure to harmful radiation.
- Improves diagnostic accuracy and treatment planning.
Conclusion
The brain MRI procedure is one of the safest and most effective ways for neurologists to diagnose, monitor, and plan treatment for neurological conditions. By producing precise, radiation-free images, it plays a critical role in modern neurology.
At Venkateshwar Hospital, patients benefit from advanced MRI technology and expert care, ensuring accurate results and comfort. If you experience unexplained neurological symptoms, your doctor may recommend a brain MRI procedure to identify the cause and guide treatment.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. Is a brain MRI painful?
No, a brain MRI is not painful. You may feel some discomfort from lying still during the scan and due to the loud noises, but the procedure itself does not cause any pain.
2. How long does it take to get results?
In most cases, results are available within 24 to 48 hours. However, the exact time can depend on the hospital’s process and the urgency of your case.
3. Can you eat before a brain MRI?
Yes, for a standard brain MRI, you can usually eat and drink as usual. If your scan requires contrast dye, your doctor may give specific instructions.
4. Is it safe during pregnancy?
A brain MRI is generally considered safe during pregnancy as it does not use radiation. However, doctors usually avoid doing MRIs in the first trimester unless necessary.
5. What is a brain MRI procedure?
The brain MRI procedure involves lying on a table that slides into a large machine shaped like a tunnel. The scanner uses magnetic fields and radio waves to capture detailed images of the brain. You need to stay still while the pictures are taken, and in some cases, contrast dye may be used for more precise results.
6. Why would a neurologist recommend a brain MRI?
A neurologist may recommend a brain MRI to diagnose conditions like stroke, brain tumours, aneurysms, multiple sclerosis, infections, or unexplained headaches and seizures.
7. How long does a brain MRI take?
A brain MRI usually takes 30 to 60 minutes. If contrast dye is used, it may take slightly longer.
8. What does a brain MRI show?
A brain MRI shows highly detailed images of the brain and surrounding structures. It can reveal abnormalities such as tumours, bleeding, stroke damage, nerve issues, or structural problems.
9. Are there any side effects of a brain MRI?
A standard brain MRI has no significant side effects. If contrast dye is used, some people may experience mild reactions such as headache, nausea, or dizziness. Serious side effects are infrequent.
Medically Reviewed by — Dr. Dinesh Sareen (Director – Neurology)